In this 12-minute article, The X Project will answer these questions:
I. Why this article now?
II. What strategic security objectives are driving the expansion of advanced nuclear technology?
III. How is regulatory reform designed to stimulate the nuclear energy sector?
IV. How does the U.S. plan to reinvigorate the nuclear industrial base?
V. How will the testing and deployment of advanced reactors be expedited?
VI. How will workforce development align with these nuclear initiatives?
VII. How will these combined executive orders transform America's nuclear energy landscape and its global strategic position?
VIII. How will America's nuclear energy landscape and its global strategic position be transformed?
IX. What does The X Project Guy have to say?
X. Why should you care?
Reminder for readers and listeners: nothing The X Project writes or says should be considered investment advice or recommendations to buy or sell securities or investment products. Everything written and said is for informational purposes only, and you should do your own research and due diligence. It would be best to discuss with an investment advisor before making any investments or changes to your investments based on any information provided by The X Project.
I. Why this article now?
Last weekend, as I reviewed my discretionary investment account, which reflects the investment themes I discuss in many of my articles, I noticed that several of my uranium-related stocks and ETFs had increased significantly. For example, the Global X Uranium ETF (URA) was up 11% on Friday, May 23rd, compared to the previous day. A week later, on this past Friday, it is still up 12% from Thursday, May 22nd. What happened?
On Friday, May 23, 2025, President Trump signed four executive orders:
REFORMING NUCLEAR REACTOR TESTING AT THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
DEPLOYING ADVANCED NUCLEAR REACTOR TECHNOLOGIES FOR NATIONAL SECURITY
While I enjoyed reading each of these executive orders, I understand not everyone has the time or the interest that I do, which is why The X Project curates, summarizes, distills, and synthesizes knowledge & learning at the interseXion of economics, geopolitics, money, interest rates, debts, deficits, energy, commodities, demographics, & markets - helping you know what you need to know.
II. What strategic security objectives are driving the expansion of advanced nuclear technology?
The executive orders explicitly outline national security as the core motivation behind the accelerated adoption of advanced nuclear reactor technologies. The United States recognizes vulnerabilities in its current energy supply, especially at critical defense installations and national security facilities. Reliable, resilient, and high-density power sources, such as advanced nuclear reactors—including Generation III+, small modular reactors, and microreactors—are deemed essential for ensuring the uninterrupted operation of artificial intelligence computing infrastructure, defense installations, and national laboratories, thereby reducing strategic risks related to energy disruptions.
Moreover, these orders emphasize geopolitical implications. As adversaries rapidly expand their nuclear capabilities globally, the U.S. risks ceding technological dominance if it does not swiftly deploy its advanced nuclear systems domestically and internationally. Consequently, reinforcing the nation's energy resilience directly aligns with broader national security interests, ensuring operational readiness and maintaining technological superiority in a competitive global environment.
To support this strategic direction, the government intends to leverage all its authority to facilitate private sector investment and innovation. This policy approach integrates military requirements with broader energy strategies, aiming to enhance the security and efficiency of both defense and civilian infrastructure. Collaboration among federal departments—Defense, Energy, and State—is highlighted as crucial, ensuring the coordinated development of regulatory frameworks and the effective deployment of advanced reactors at both military and civilian sites.
III. How is regulatory reform designed to stimulate the nuclear energy sector?
Regulatory reform is central to these executive orders, with a particular focus on overhauling the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). Historically, the NRC has been criticized for its conservative and prolonged approach to licensing nuclear reactors, which has significantly limited new developments. The reform mandates a comprehensive reevaluation of the NRC's regulatory process to expedite approvals, set clear deadlines, and establish transparent, fixed timeframes for licensing new reactors and renewing existing ones, thereby facilitating quicker industry responses and project planning.
The reforms specifically target NRC practices that impose unnecessarily stringent radiation safety standards based on outdated models, such as the Linear No-Threshold (LNT) hypothesis, which the administration argues lack solid scientific grounding. Replacing these with more realistic, scientifically sound, and risk-based standards will significantly lower barriers and costs associated with new nuclear projects. The introduction of expedited pathways for technologies already tested by the Department of Defense and Energy further exemplifies this targeted effort to streamline regulation.
Additionally, these reforms include organizational restructuring within the NRC, downsizing of redundant advisory bodies, and increased accountability through enforceable deadlines and fee caps. Collectively, these reforms are designed to create an efficient regulatory environment that encourages rapid technological deployment, promotes safety based on realistic risks, and enables the U.S. to reclaim its global leadership in nuclear energy production and innovation.
IV. How does the U.S. plan to reinvigorate the nuclear industrial base?
Reinvigoration of the U.S. nuclear industrial base is explicitly prioritized within these executive orders, emphasizing the need for rapid, decisive action to rebuild and sustain domestic nuclear capabilities. The erosion of the nuclear fuel cycle infrastructure has significantly heightened American reliance on foreign sources of uranium enrichment and conversion services, presenting a strategic vulnerability that these orders directly address.
The plans outlined involve expanding domestic capabilities in uranium enrichment and fuel fabrication, strategically leveraging federal authorities, such as the Defense Production Act, to form cooperative agreements with private sector firms. These agreements aim to stimulate investment, production, and infrastructure development, with a focus on securing and stabilizing domestic nuclear fuel supplies. Moreover, a detailed roadmap and policy are to be developed to manage spent nuclear fuel and promote recycling technologies, thereby enhancing sustainability and economic efficiency.
Further efforts include prioritizing support for restarting previously closed nuclear plants, uprating existing reactors, and facilitating the construction of new large and advanced reactors. Financial incentives and loan programs administered by the Department of Energy are set to encourage significant industry participation. Ultimately, these actions aim to establish the U.S. as the premier global hub for nuclear technology and innovation, supported by a robust and self-sufficient nuclear supply chain.
V. How will the testing and deployment of advanced reactors be expedited?
Expediting the testing and deployment of advanced nuclear reactors is a critical element of the administration’s strategy. It acknowledges decades of stagnation and aims to revitalize testing through swift procedural changes and administrative streamlining, primarily at facilities like the Idaho National Laboratory. The Department of Energy (DOE) is directed to redefine regulations and expedite approvals, ensuring that new reactors achieve operational status rapidly, ideally within two years following the submission of applications.
A specific pilot program has been introduced to facilitate reactor construction and operation outside traditional laboratory settings, enhancing flexibility and practical testing opportunities. This program sets ambitious targets for achieving criticality, reflecting a clear administrative commitment to accelerating development timelines and overcoming bureaucratic inertia. Environmental review processes under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) are also streamlined, which further accelerates approvals and reduces project delays.
Moreover, the orders require interagency collaboration, particularly between DOE and the Department of Defense, to leverage each other's testing results and expedite approval processes. This integrated testing and deployment model aims to eliminate redundancy, significantly cut development timelines, and swiftly bring advanced reactors from concept to operational readiness, enhancing both technological innovation and energy security.
VI. How will workforce development align with these nuclear initiatives?
The orders explicitly identify workforce development as a critical component for sustaining long-term growth in the nuclear industry. They call for integrating nuclear engineering and related skills into priority education initiatives, mainly through Registered Apprenticeships and Career and Technical Education programs. Enhanced funding and policy direction are provided to ensure increased enrollment in these specialized programs, reflecting the immediate need for qualified professionals.
Further directives instruct the Department of Labor and Education to perform gap analyses, establish apprenticeship programs, and prioritize funding streams dedicated explicitly to nuclear energy training. Collaboration with industry and educational institutions aims to create a robust pipeline of skilled professionals who are ready to support the expansion of the nuclear sector. Involving Department of Energy National Laboratories as centers of advanced training and research also helps ensure students and military personnel gain critical, real-world experience.
Overall, this workforce development strategy is designed to secure long-term industry sustainability by addressing skills shortages, fostering industry-academic partnerships, and embedding nuclear energy careers prominently within the nation's broader technical education framework.
VII. What role will international cooperation and export strategies play?
International cooperation and exports are key pillars of the strategic nuclear policy articulated by these executive orders. Aggressive diplomatic efforts, led by the Department of State, aim to secure new international Agreements for Peaceful Nuclear Cooperation (123 Agreements) and renegotiate existing ones to expand U.S. market access globally. By committing resources to enhance competitiveness in nuclear exports, the U.S. intends to position itself as a preferred global supplier, strengthening alliances and countering geopolitical rivals.
The strategic use of financing institutions, such as the Export-Import Bank and the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation, combined with enhanced advocacy and diplomatic support, aims to level the global playing field for American companies. These strategies focus on facilitating entry into rapidly growing nuclear markets, particularly in regions strategically significant to U.S. interests, thereby extending U.S. influence and promoting the global adoption of American standards and safety practices.
This approach not only bolsters the domestic economy through increased exports but also reinforces U.S. leadership in international nuclear governance, nonproliferation, and safety standards, creating a secure and predictable international environment for civil nuclear expansion.
VIII. How will America's nuclear energy landscape and its global strategic position be transformed?
Collectively, these four executive orders represent a comprehensive overhaul designed to reestablish the United States as a dominant global leader in nuclear energy and significantly enhance national security. By systematically addressing regulatory bottlenecks, modernizing reactor testing and deployment practices, expanding domestic nuclear infrastructure, and fostering international nuclear exports, these policies aim to reverse decades of stagnation in nuclear energy development. Such coordinated reforms are poised to rapidly scale nuclear capabilities, increase resilience in critical energy infrastructures, and dramatically bolster the nation’s strategic autonomy in energy resources.
These orders notably realign regulatory practices with realistic risk assessments, reducing bureaucratic barriers that have historically hindered progress. By restructuring and streamlining the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, the U.S. government acknowledges past inefficiencies and sets ambitious timelines for licensing new and existing reactors. This approach, coupled with targeted financial incentives, workforce training initiatives, and enhanced collaboration between the defense and energy sectors, lays a robust foundation for rapid industrial growth and technological advancement in the nuclear energy sector. This realignment strategically positions America’s nuclear industry to accelerate both domestic expansion and global market penetration.
Internationally, the coordinated push to increase nuclear exports and aggressively negotiate cooperation agreements underscores the intent to leverage nuclear energy as a tool of geopolitical influence. Establishing advanced nuclear technologies domestically and exporting these innovations internationally serves dual purposes: it counters geopolitical rivals by reducing global reliance on their nuclear technology, and simultaneously strengthens alliances by offering safe, reliable, and advanced energy solutions. By pursuing this integrated domestic and foreign nuclear strategy, the executive orders effectively aim to reposition the United States at the forefront of a secure, innovative, and strategically advantageous global nuclear order.
IX. What does The X Project Guy have to say?
HOORAY!!!
To understand my excited and jubilant response to these executive orders, here are the prior articles I have written about energy:
Energy Transition Crisis - A summary of the 8-part docuseries by Erik Townsend
"Electravision": A Summary of Michael Cembalest's 14th Annual Energy Paper
The Case for Uranium: Why it looks bullish and why we should embrace it?
“Bettering Human Lives”: Liberty Energy’s Report Providing Insight on Chris Wright’s Views
All of these articles are still relevant and worthy of reading or re-reading.
X. Why should you care?
Borrowing from my first article on energy above:
Let’s look at a few charts that inspired The X Project to include energy as a focus in its mission. First is this chart that was floating around X/Twitter that makes an obvious point that most people probably miss:
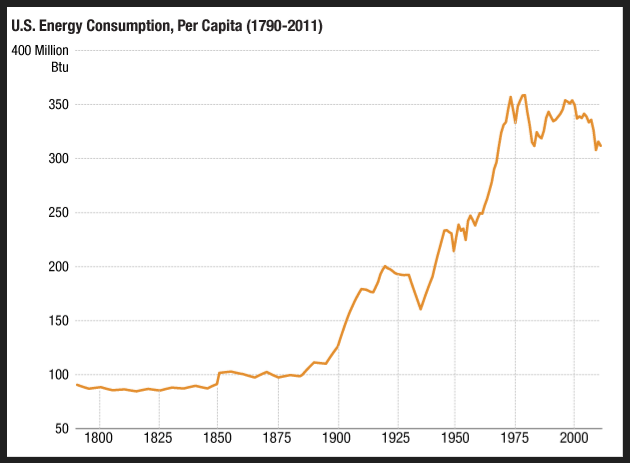
Second is this chart that was also floating around X/Twitter and is believed to have originated from an NPR story from 2013:
In this second chart, one can see the expansion of coal use in the mid-1800s, followed by the discovery and use of oil at the end of the 19th century, the Great Depression in the 1930s, and then a steady increase in energy consumption per capita up until the 1970s at which point energy use per capital has chopped sideways to lower.
This brings us to the third chart courtesy of Mike Green at Simplify Asset Management, which came from his Substack article titled Is the Age of Deprivation Coming to a Close?
This chart explains so much that it is hard to know where to begin. To quote Mike directly: “This is the key story of our lifetimes. It’s why housing is unaffordable, why medical care is expensive, and why many fear their children’s lives will be worse than their own. As noted in the Founder’s Fund manifesto, ‘The correlation between wealth and energy use is extremely high, and whichever direction the causality runs, a future world of greater material comfort is going to be one that uses more energy.’ By extension, a world in which LESS energy is used per capita is a world of LESS material comfort.”
Thank you for your subscription, especially if you are a paying subscriber. Your support is everything to The X Project and is greatly appreciated. If you agree, please take a moment to hit the like button and share your positive comments about my articles, assuming you have something constructive to say.